Virtual Master School
Portal for Open Educational Resources (OER)
Project Reference: 619034-EPP-1-2020-1-UA-EPPKA2-CBHE-JP
Virtual Master School
Digital transformation of the higher education requires systematical approach not only for the development of the educational resources, but also for the delivery procedure.
The questions which need to be answered:
- how to integrate variety of different master programs ?
- how to synchronize different semester calendars for Universities from different countries?
- how to recognize results, achieved by students in different exchange programs?
WORK4CE Virtual Master School concept is the concept for cross-border cooperation between the High Educational Institutes, aimed to provide the basis for the border free students access to the knowledge and is based on integration of several approaches:
- the curricula integration model from cross-border Master School of the European Partnership for Project and Innovation Management (EuroPIM) [1].
- event based project implementation Model [2].
- Agile project management including cross-border monthly meeting.
- Open Communities of Practice (OpenCops) concept for joint content development and delivery.
- E-learning Didactic Concept for online material development and delivery.
The EuroPIM consortium is running 8 connected Master’s programs which are connected with cooperation formats [1]:
- Modules, which students attend at home universities. Modules developed locally in each university.
- Joint modules which are shared by two or more partner universities. The module development is done by cross-border teams.
- Summer Schools (or Spring, Autumn, Winter) where students and lecturers travel to one partner university and run workshops on different topics.
- Joint supervision of theses and student projects, where projects can be conducted by cross-border teams. 3d-4th semesters.
- Regular exchange semesters at partner universities which are used to offer specializations to students which are not offered by their home university.
- Double degrees which are based on module recognition and jointly supervised elements, e.g. projects, theses.
- Master student conferences where students (and lecturers, PhD students) present and publish their work in a relaxed environment.
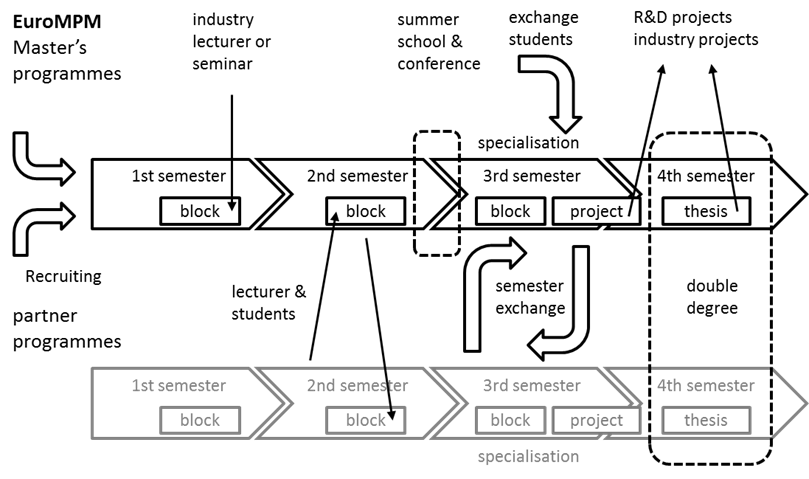
The EuroPIM Master School is (still) mainly done by real classroom activities, real travel, teamwork in real, physical presence.
This concept was selected for the WORK4CE consortium as from the EuroPim Master School participating 3 partners UPV/EHU Bilbao in Spain, FH Dortmund, Germany, who are successfully practicing this concept for several years.
For the synchronizing different semester calendars from different partner universities to be possible to provide joint events and workshops the cumulative project execution based on events as outputs was selected [2].
The main component is the portfolio of events [2]: all events and interactions are scheduled in an annual calendar which is made available to all involved parties. Furthermore, the events in the calendar are the basis for the budget estimation (based on the estimated number and duration of the mobilities) for the event which serves as the bottom-up planning data for the annual budget.
To implement Virtual Master School concept the WORK4CE Team need to complete following steps:
- Define connected Master Curricula in all 9 Universities.
- Define the Joint modules which will be implemented from the 9 Modules of the project.
- Define the Portfolio of actual and virtual events for the consortium.
- Define funding models for short and long exchange programs.
- Define the plan of the double degree implementation between the partner universities.
- Set the Digital Portal for the joint educational infrastructure.
Reference:
- C. Wolff, C. Reimann, E. Mikhaylova, A. Aldaghamin, S. Pampus and E. Hermann, “Digital Education Ecosystem (DEE) for a Virtual Master School,” 2021 IEEE International Conference on Smart Information Systems and Technologies (SIST), Nur-Sultan, Kazakhstan, 2021, pp. 1-7, doi: 10.1109/SIST50301.2021.9465914.SIST-Wolff_etal_final3.pdf
- O. Mikhieieva, A. Nuseibah, C. Decelis Grewe, C. Wolff and C. Reimann, “Implementing a project management approach for public-funded projects in HEIs,” 2017 9th IEEE International Conference on Intelligent Data Acquisition and Advanced Computing Systems: Technology and Applications (IDAACS), Bucharest, Romania, 2017, pp. 247-252, doi: 10.1109/IDAACS.2017.8095085.
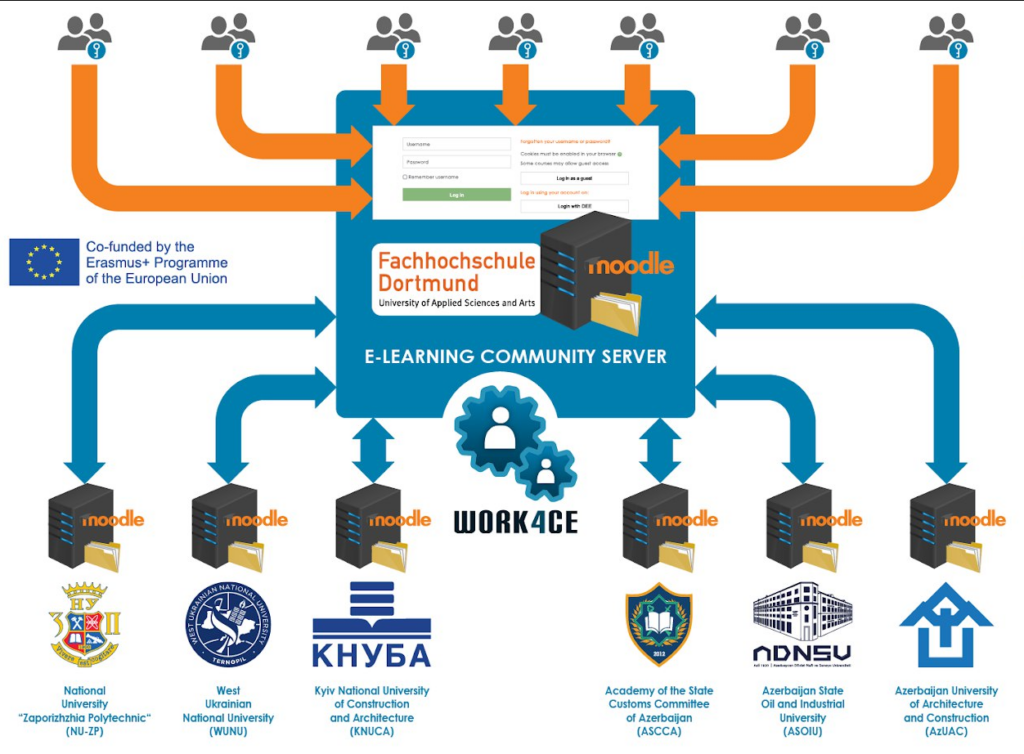
Cross Border Infrastructure
Infrastructure elements:
- Moodle distance learning system;
- Campus Connect plugin;
- E-learning Community Server.
Open Educational Resources
Open Educational Resources (OER) are freely available and openly licensed documents and media that are useful for teaching, learning, education, assessment, and research. The creation and dissemination of OER helps to broaden access and participation in education by removing barriers and making learning accessible to all.
The 5R Activities of OER:
- Retain: Make, own, and control your own copy of the content
- Reuse: Use the content as-is
- Revise: Adapt, adjust, modify, improve, or alter the content
- Remix: Combine the original or revised content with other OER to create something new
- Redistribute: Share your copies of the original content, revisions or remixes with others
Contact
Galyna Tabunshchyk galina.tabunshchik@gmail.com
News & Events
- |
- News
As part of pilot training under the Erasmus+ KA2: Capacity Building in Higher Education “Cross-domain
Funded by

Next Events
Repository of Open Educational Resources (OER)
Data Analytics for Work
Unsupervised learning. Cluster Analysis. Part I.
Unsupervised learning. Cluster Analysis. Part II.
Industry 4.0
Technical course "IoT (Internet of Things)"
Lecture 1. Introduction to the course
Lecture 2. IoT systems prototyping based on online engineering tools
Lecture 3. Embedded systems as the basis of IoT infrastructure
Lecture 4. Cloud and wireless technologies for IoT applications
Practical part. Tinkercad overview
Technical course"Additive manufacturing"
Lecture 1. Introduction to the course
Lecture 2. Technologies of additive manufacturing
Lecture 3. Additive manufacturing design guidelines
"Building Information Modelling (BIM)" Technical course, elective
Lecture 1.
Distributed Teams
About the Curriculum "Project Management"
About the Distributed Teams Module
Elective course I. Hiring
Elective course II. Using software for virtual communication
Elective course III. Psychological type
Elective course IV. Cultural diversity
Elective course V. Time management
Elective course VI. Motivation aspects
Elective course VII. Personal productivity
Elective course VIII. Constructive communication
Elective course IX. Facilitation
About the Curriculum “Project Management” for the Speciality 122 “Computer Science”
About the Distributed Teams Module
Elective course I. Hiring
Elective course II. Using software for virtual communication
Elective course III. Psychological type
Elective course IV. Cultural diversity
Elective course V. Time management
Elective course VI. Motivation aspects
Elective course VII. Personal productivity
Elective course VIII. Constructive communication
Elective course IX. Facilitation
Managing Digital Change
Digital Transformation Maturity Models
Life Cycle Thinking and Sustainable Management
Digital Sustainability Canvas
Developing Digital Business Ecosystems
Digital Business Canvas
Data Analytics for Work
Unsupervised learning. Cluster Analysis
Part I.
Unsupervised learning. Cluster Analysis
Part II.
Industry 4.0
Technical course "IoT (Internet of Things)"
Lecture 1
Lecture 2
Lecture 3
Lecture 4
Technical course"Additive manufacturing"
Lecture 1
Lecture 2
Lecture 3
Lecture 1
Distributed Teams
About the Curriculum “Project Management” for the Speciality 122 “Computer Science”
About the Distributed Teams Module
Elective course I. Hiring
Elective course II. Using software for virtual communication
Elective course III. Psychological type
Elective course IV. Cultural diversity
Elective course V. Time management
Elective course VI. Motivation aspects
Elective course VII. Personal productivity
Elective course VIII. Constructive communication
Elective course IX. Facilitation
Managing Digital Change
Digital Transformation Maturity Models
Digital Transformation Maturity Models
Life Cycle Thinking and Sustainable Management
Digital Sustainability Canvas
Digital Sustainability Canvas
Digital Sustainability Canvas
Digital Sustainability Canvas
Digital Sustainability Canvas
Developing Digital Business Ecosystems
Digital Business Canvas
Digital Business Canvas
Digital Business Canvas


